What is a photovoltaic energy storage system?
A photovoltaic energy storage system is a combination of equipment and technology that converts solar energy into electrical energy to supply household appliances while storing the excess for use at night or in the absence of utility power.

What is it and what are the main components?
1. Photovoltaic module: consists of several photovoltaic modules (also known as solar panels) that are responsible for capturing sunlight and converting it into direct current.
2. Racking, accessories and cables: used to fix the solar panels and transport the generated DC power to the inverter.
3. Inverters (grid-connected and off-grid inverters): Alternating current (AC) power is created by inverting the direct current (DC) power generated by solar panels, and store the excess power in an energy storage system, which can also be connected to the city grid.
4. Energy storage devices: Usually refers to batteries, such as lithium batteries and other types of batteries, which store electricity generated by solar energy that is not used immediately through an inverter for later use.
5. EMS and BMS: EMS is the system that monitors and manages the operation of the entire system to ensure that all parts work efficiently and safely. BMS is the management system of the storage battery, optimising and controlling the charging and discharging of the battery.
6. Convergence box: including all kinds of protection equipment and switches, such as surge protection (lightning protection) in the middle of the solar access inverter, fuses, DC circuit breakers, utility input circuit breakers, uninterruptible power supply output circuit breakers and so on.
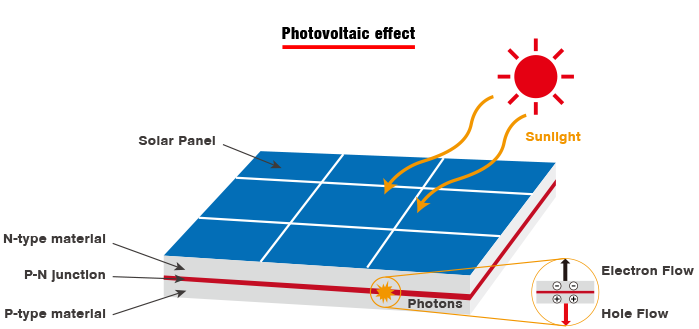
Photovoltaic effect, how to get electricity from solar energy
1. Absorption of photons: When sunlight (including other light sources) hits the material (silicon) of the solar panel, the energy of the photons is absorbed by the semiconductor material.
2. Excitation of electrons: The absorbed photon energy causes the electrons in the semiconductor to jump from the valence band to the conduction band, changing them from a bound state to a free state.
3. Generation of electron-hole pairs: When an electron is excited into the conduction band, it leaves a hole in the valence band. This electron and hole form an electron-hole pair.
4. Establishing an electric field: P-type and N-type regions are usually present in photovoltaic materials, and at the junction of these two regions (i.e., the PN junction), an internal electric field is formed.
5. Driving the flow of electrons: This internal electric field drives the free electrons to move towards the N-type region and the holes to move towards the P-type region, and this movement creates a current.
6. Collecting the current: Through an inverter, this current is converted into AC or DC electricity and stored in the energy storage system for later use.
How grid-connected and off-grid inverters work and their mode of operation
1. The grid-connected inverter converts the DC power generated by solar panels into suitable bus voltage for inverter through MPPT module, and then converts it into AC power through electronic components to supply household appliances, and if there is excess power, it will be converted into the same voltage as that of the storage system and charged into the storage system for backup, and if there is excess power, it will be reversed and integrated into the power grid.
2. PV energy storage systems have self-generation and self-consumption modes, peak-shaving and valley-filling modes, and battery-priority modes.
Self-generation and self-use mode: the electricity generated by solar panels is converted into alternating current (AC) and directly supplied to household appliances, while the excess is charged into the storage system; if the current generated by solar panels is not enough to be used by household appliances, it is replenished using the city power grid.
Peak Shaving and Valley Filling Mode: At the set trough time, the AC power from the city grid will be converted into DC power and charged into the energy storage system; at the set peak time, the DC power in the energy storage system will be converted into AC power to be supplied to household appliances; if the battery power is insufficient, it will be supplemented by the city grid.
Battery Priority Mode: No matter what the situation is, first ensure that the power of the energy storage system is full, when the solar energy generates more power, it will be directly converted into AC power for home battery use, and when the grid-connection function is turned on, the excess will be added to the city grid.
How to design and calculate how many W solar panels to install
Solar panel: LESSO 550W
Size: L 2278 x 1134mm approx. 2.6 sq. ft.
Weight: 28kg
Power: 550W
Area calculation formula:
Note: Support solar panels below 7KW
Total power of solar panel: 550W*12=6.6KW
Required roof area: 12 x 2.6 sq. ft. = 31.2 sq. ft.
Daily power generation calculation:
Take Wenzhou, China as an example, peak sunshine 3.77 hours, per watt per year power generation 1.088KWH, annual effective use of hours 1087.08 hours Installation angle: 18 degrees
Peak daily power generation = 6.6KW x 3.77H = 24.88KWH
Annual power generation = 6.6KW x 1087.08H = 7174.728KWH







